Types of Environmental Audits
Companies with Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) responsibilities typically conduct two types of environmental audits:
1. Environmental Management System (EMS) Audits
These audits review how well an environmental management system is working.
They measure performance against standards like ISO 14001.
The goal is to find gaps in system implementation.
2. Environmental Compliance Audits
These audits check compliance with environmental laws and regulations.
They may include:
This article focuses on environmental compliance audits and how audit protocols support them.
EPA Guidance on Environmental Audits
The EPA encourages companies to use environmental audits.
Audits help organizations:
-
Meet environmental laws and regulations
-
Find and fix compliance issues
-
Identify environmental risks that may not be regulated
According to the EPA, an environmental audit should be:
-
Systematic
-
Documented
-
Periodic
-
Objective
Audits should review facility operations and practices tied to environmental requirements.
What Is an Audit Protocol?
An audit protocol helps plan and perform environmental compliance audits.
It defines site-specific audit activities and outlines what to review.
Audit protocols include tools that guide auditors through the process.
Common Components of an EPA Audit Protocol
-
Guidance on key regulatory requirements
-
Definitions of regulatory terms
-
Summaries of applicable federal environmental laws
-
A detailed audit checklist
The Audit Checklist
The checklist is the most actionable part of the audit protocol.
It tells auditors exactly what to evaluate.
Checklist responses may include:
Despite different formats, many audit requirements are consistent across organizations.=
Key Elements of an Environmental Audit
Most environmental compliance audits include three core activities:
Records Review
Physical Inspections
Interviews
Addressing Audit Findings
After the audit, the protocol helps guide corrective actions.
Issues found during the audit are analyzed and documented.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis identifies why an issue occurred.
It focuses on preventing repeat problems, not just fixing symptoms.
Corrective Actions
-
Non-conformances are grouped into findings
-
Findings are assigned corrective action tasks
-
Actions are tracked until resolution
A structured audit process helps organizations improve compliance and reduce environmental risk over time.
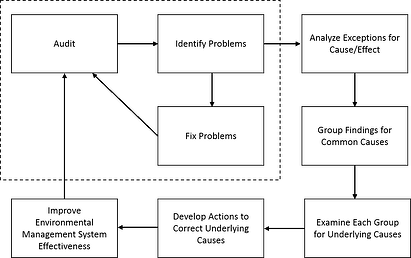
Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under the Stormwater Program, iv
Benefits of a Consistent Audit Process
When organizations follow a structured audit process, they see stronger compliance and better environmental performance.
The benefits often extend beyond a single site or department.
Organization-Wide Impact
Improvements identified at one facility can be applied across the company.
For example:
-
An audit uncovers ways to reduce energy use
-
Waste reduction opportunities are identified
-
The same changes are rolled out at other locations
This approach helps organizations lower costs and improve performance at scale.
Compliance as a Starting Point
Because of these benefits, the EPA encourages companies to view compliance as a baseline, not the end goal.
Voluntary environmental audit programs help organizations go beyond minimum requirements.
The Role of Self-Assessments
One effective way to support this approach is through regular self-assessments.
Self-assessments allow organizations to:
-
Prepare for formal audits
-
Identify non-conformances early
-
Address issues before they become violations
-
Reduce risk to human health and the environment
Think of self-assessments as a low-risk way to test and improve compliance programs.
How Software Supports Environmental Audits
Audit management software simplifies and strengthens the audit process.
It helps teams work more efficiently and stay organized.
Key Capabilities of Audit Management Software
-
Centralized audit planning and scoping
-
Digital audit checklists and protocols
-
Automated findings and corrective action tracking
-
Audit report generation within the system or as PDFs
An automated system connects each step of the audit lifecycle in one place.
Why Audit Protocol Management Matters
Whether audits are conducted internally or by third parties, managing audit protocols is essential.
Strong protocol management helps organizations:
-
Maintain regulatory compliance
-
Improve environmental management system performance
-
Ensure audits are consistent and repeatable
With the right tools and processes in place, audits become more effective and easier to manage over time.
[i] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under CERCLA, ii
[ii] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits for Hazardous Waste Generators under RCRA, iii
[iii] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under CERCLA, v
[iv] Protocol for Conducting Environmental Compliance Audits under the Stormwater Program, i
